CGM: Continuous Glucose Monitor
Today’s CGM—continuous glucose monitor—technology put diabetes management into the 21st century. This small wearable device provides people with diabetes the information they need to make daily management decisions.
Improving both our short- and long-term health and safety, CGMs should be considered the standard of care for anyone of any age with any type of diabetes.
What is a CGM?
A CGM is a small wearable device that tracks your blood glucose levels in real-time throughout the day and night. CGMs measure the glucose (sugar) in the interstitial fluid of your body fat compared to your blood glucose monitor (BGM) which measures the glucose in your blood.
At any moment—without pricking your finger—you can see what your blood glucose level is. You can also see what direction it’s headed in thanks to simple up, down, or sideways arrows.
With personalized settings, CGMs can alert you to high or low levels while also charting your blood glucose levels about every five minutes on a graph on your smartphone or separate receiver device.
Compared to checking your blood sugar with a drop of blood on a test strip, the information a CGM can provide both you and your healthcare team can have a huge impact on your diabetes management. CGM technology can help you make more thoughtful decisions around food, exercise, insulin and medications. The insights you gain from using a CGM can improve your safety and help you reach your A1c and time-in-range goals.
Watch this video to learn more about the differences between readings from your CGM vs. your BGM.
How a CGM works
While each brand of CGM technology works slightly differently, they have many similarities. (*Most of the details described below do not apply to Senseonics’ implantable Eversense CGM technology.)
A CGM consists of three basic parts:
- Receiver (or smartphone): A device where you can check your current blood glucose level, look at past data and view your blood glucose trends and patterns. This may be an app on your smartphone or a separate device.
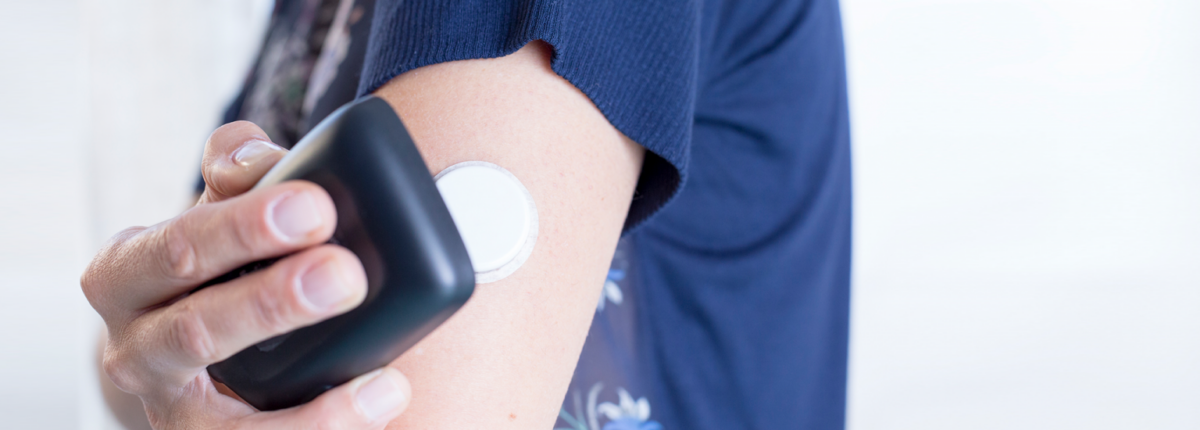
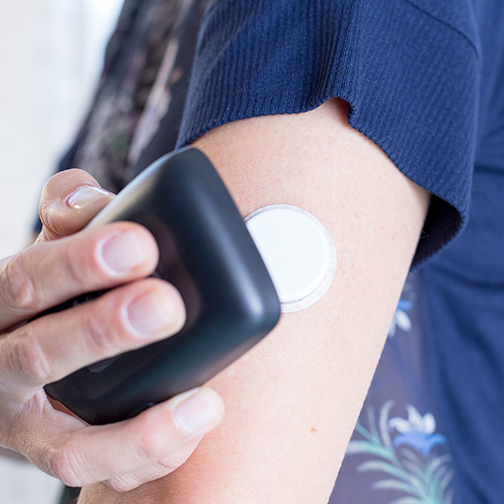
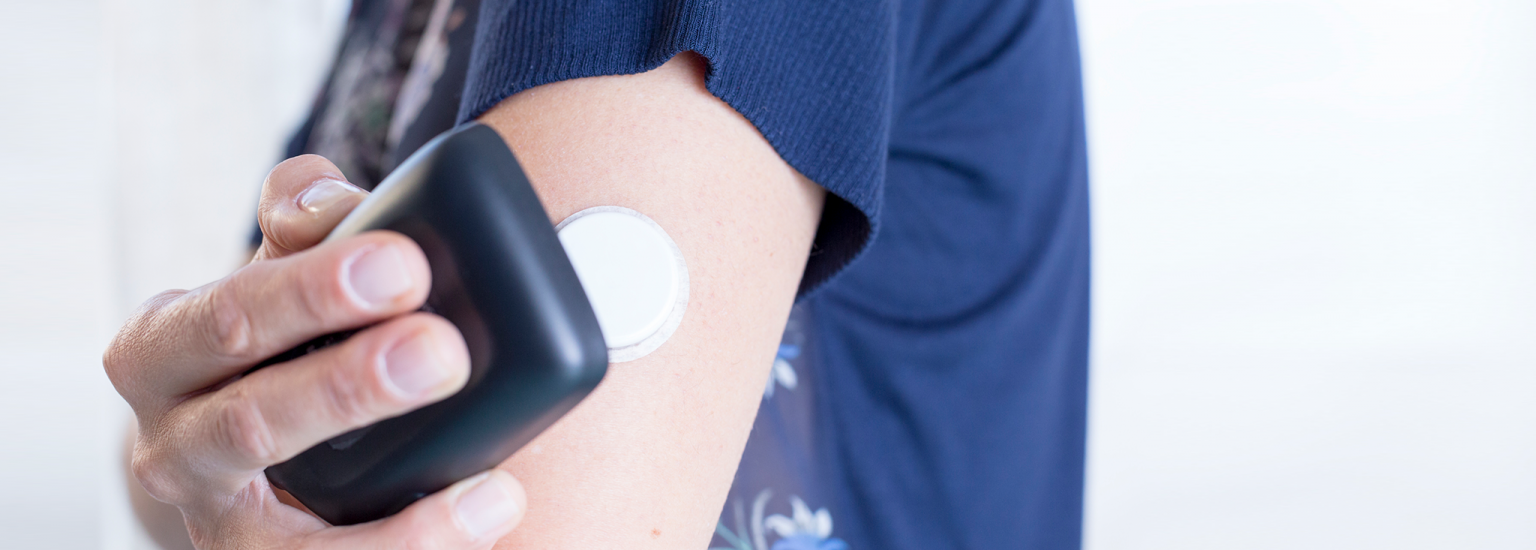
- Sensor: The device that measures blood glucose. It contains a very thin wire that is inserted under the skin in subcutaneous tissue (body fat). It’s typically painless to wear and remains in the skin for several days. Users wear them on the stomach and the back of the arms or legs, or according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Transmitter: Some CGM systems, like Dexcom, also have a small piece that fits onto the sensor and sits above the skin. This reusable transmitter sends blood glucose data wirelessly to your display device.
The process of inserting the CGM sensor is easy and virtually painless. It can easily be done at home and takes just a few minutes from start to finish. Most CGM sensors need to be replaced about every two weeks—this varies slightly depending on brand and model.
The benefits of a CGM
A few of the benefits of using a CGM include:
- Seeing your blood glucose level at any moment without pricking your finger
- Seeing the direction of your blood glucose level: rising/falling, gradually/quickly
- Learning how/when your body responds to food, activity, insulin, medication, hormones, stress, etc.
- Customizable settings that alert you when your blood sugar falls below a certain level
- Customizable settings that alert you when your blood sugar rises above a certain level
- Catching and treating high blood glucose levels sooner
- Catching and treating low blood glucose levels sooner
- Helping you reach your overall A1c and blood sugar goals
- Learning what percentage of the day you are in/above/below your goal ranges (also known as “time-in-range” or TIR)
- Integrating your CGM with your insulin pump (with additional features for closed-loop systems)
- Sharing your CGM data with your healthcare team easily from the app on your smartphone
- Sharing your real-time CGM data with family or friends to see at any time on their smartphone
- Reviewing your blood glucose levels at any time with helpful graphs and reports
How do I get a CGM?
Getting a CGM starts with asking your doctor to write the prescription. Talk to your doctor about your device options and decide together which might be best for you. (Scroll further on this page for detailed tips on getting a CGM.)
Research on the Benefits of Using a CGM
- Research shows people with type 2 diabetes who are on multiple daily insulin injection therapies (MDI) and used a CGM lowered their average A1C from 8.5 percent to 7.7 percent.
- In contrast, those who tracked their blood glucose using a standard BGM were only able to lower their A1C from 8.5 percent to 8.0 percent. Better management decreases the risks of complications.
CGMs Available Today
Here are today’s available CGM brands and models. This technology has evolved rapidly over the last decade, improving in ease-of-use, accuracy and connectivity with other technology.
Abbott: Freestyle Libre & Libre 2►
Dexcom: G6►
Medtronic: Guardian Connect►
Watch this video to learn more about the differences between blood glucose readings and sensor readings, watch the video by FreeStyle Libre system below.
Getting a CGM starts with asking your doctor to write the prescription. Talk to your doctor about your device options and decide together which might be best for you.
Check what brands are covered under your insurance plan. To check your eligibility for a CGM under Medicare, please consult your provincial or territorial health insurance plan.
Some brands also offer complimentary trial periods for new users, like the Hello, Dexcom.